AI Models in Brain Tumor Detection: Achieving High Accuracy with MRI Data
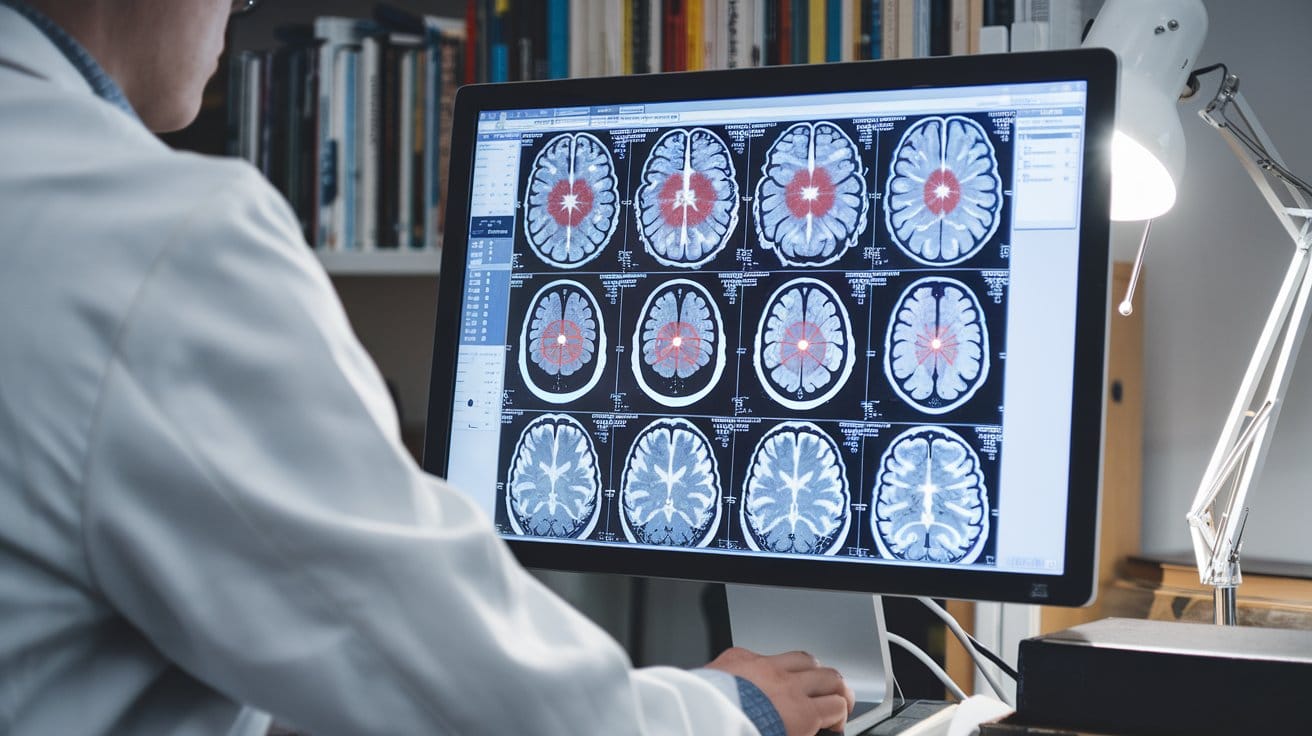
The application of artificial intelligence (AI) in medical imaging, particularly in the detection and classification of brain tumors using magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), has seen significant advancements. AI models, especially those leveraging convolutional neural networks (CNNs) and transfer learning, have demonstrated remarkable accuracy in distinguishing brain tumors from healthy tissue.
AI in Brain Tumor Detection
Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs)
CNNs have revolutionized the field of medical imaging by enabling the automatic extraction of features from complex datasets, such as MRI scans. Unlike traditional image processing techniques that require manual feature engineering, CNNs learn features directly from the data, which is particularly beneficial for analyzing the intricate and varied nature of brain tumors.
The use of CNNs in brain tumor detection involves a multi-stage process that includes detection, classification, and segmentation of tumors. A study published in Scientific Reports describes a system using CNNs for the detection and classification of glioblastomas, a type of high-grade glioma, from MRI images. The system categorizes MRI images into normal, high-grade glioma, and low-grade glioma, utilizing different levels of features, including local and global paths, to enhance accuracy.